Complete Docker CLI
Docker’s purpose is to build and manage compute images and to launch them in a container. So, the most useful commands do and expose this information. Here’s a cheat sheet on the top Docker commands to know and use. Images and containers. The docker command line interface follows this pattern: docker docker images docker container. Do not expose the Docker daemon socket (even to the containers)¶ Docker socket. Docker Hub provides Docker image hosting, public or private registries, build triggers and web hooks, and integration with GitHub and Bitbucket. Docker daemon: Runs on host machine creates and manages docker objects such as images, containers, network, volume, data, etc.
Container Management CLIs
Inspecting The Container
Interacting with Container
Image Management Commands
Image Transfer Comnands
Builder Main Commands
The Docker CLI
Manage images

docker build
Create an image from a Dockerfile.
docker run
Run a command in an image.
Manage containers
docker create
Example
Create a container from an image.
docker exec
Example
Run commands in a container.
docker start
Start/stop a container.
docker ps
Manage containers using ps/kill.
Images
docker images
Manages images. Bluestacks 4 install.
docker rmi
Deletes images.
Also see
- Getting Started(docker.io)
Inheritance
Variables
Initialization
Onbuild
Commands
Entrypoint
Configures a container that will run as an executable.
This will use shell processing to substitute shell variables, and will ignore any CMD or docker run command line arguments.
Metadata
See also
Basic example
Commands
Reference
Building
Ports
Commands
Environment variables
Dependencies
Other options
Advanced features
Labels
DNS servers
Devices
External links
Hosts
sevices
To view list of all the services runnning in swarm
To see all running services
to see all services logs
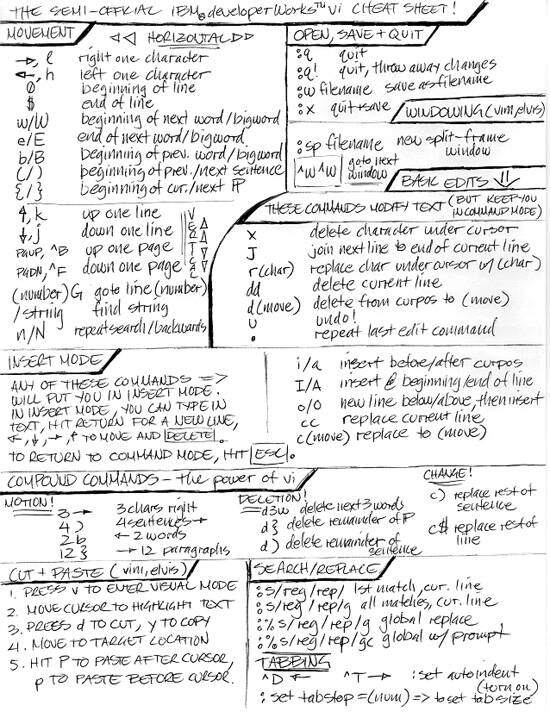 This cheat sheet is intended to be a quick reminder for the main concepts involved in using the command line program Vim (or vi) and assumes you already understand its usage. It does not cover every command in Vim, only the ones we consider to be useful for most people for the majority of.
This cheat sheet is intended to be a quick reminder for the main concepts involved in using the command line program Vim (or vi) and assumes you already understand its usage. It does not cover every command in Vim, only the ones we consider to be useful for most people for the majority of.
To scale services quickly across qualified node
clean up
To clean or prune unused (dangling) images
To remove all images which are not in use containers , add - a
To Purne your entire system
To leave swarm
To remove swarm ( deletes all volume data and database info)
To kill all running containers
Contributor -
Sangam biradar - Docker Community Leader
Docker swarm cheat sheet. List of all commands to create, run, manage container cluster environment, Docker Swarm!
Docker swarm is a cluster environment for Docker containers. Swarm is created with a number of machines running docker daemons. Collectively they are managed by one master node to run clustered environment for containers!
Manycam macos x. In this article, we are listing out all the currently available docker swarm commands in a very short overview. This is a cheat sheet you can glance through to brush or your swarm knowledge or quick reference for any swarm management command. We are covering most used or useful switches with the below commands. There are more switches available for each command and you can get them with --help
Read all docker or containerization related articles here from KernelTalk’s archives.
Docker Flags Cheat Sheet Template
Docker swarm commands for swarm management
This set of command is used mainly to start, manage the swarm cluster as a whole. For node management, within the cluster, we have a different set of commands following this section.
docker swarm init: Initiate swam cluster- –advertise-addr: Advertised address on which swarm lives
- –autolock: Locks manager and display key which will be needed to unlock stopped manager
- –force-new-cluster: Create a new cluster from backup and dont attempt to connect to old known nodes
docker swarm join-token: Lists join security token to join another node in swarm as worker or manager- –quite: Only display token. By default, it displays complete command to be used along with the token.
- –rotate: Rotate (change) token for security reasons.
docker swarm join: Join already running swarm as a worker or manager- –token: Security token to join the swarm
- –availability: Mark node’s status as active/drain/pause after joining
docker swarm leave: Leave swarm. To be run from the node itself- -f: Leave forcefully ignoring all warnings.
docker swarm unlock: Unlocks swarm by providing key after manager restartsdocker swarm unlock-key: Display swarm unlock key- -q: Only display token.
- –rotate: Rotate (change) token for security reasons.
docker swarm update: Updates swarm configurations- –autolock: true/false. Turns on or off locking if not done while initiating.
Docker swarm node commands for swarm node management
Node is a server participating in Docker swarm. A node can either be a worker or manager in the swarm. The manager node has the ability to manage swarm nodes and services along with serving workloads. Worker nodes can only serve workloads.
docker node ls: Lists nodes in the swarm- -q : Only display node Ids
- –format : Format output using GO format
- –filter : Apply filters to output
docker node ps: Display tasks running on nodes- Above all switches applies here too.
docker node promote: Promote node to a manager roledocker node demote: Demote node from manager to worker roledocker node rm: Remove node from the swarm. Run from the manager node.- -f : Force remove
docker node inspect: Detailed information about the node- –format : Format output using GO format
- –pretty : Print in a human-readable friendly format
docker node update: Update node configs- –role : worker/manager. Update node role
- –availability : active/pause/drain. Set node state.
Docker swarm service commands for swarm service management
Docker service is used to create and spawn workloads to swarm nodes.
Docker Build Flags
docker service create: Start new service in Docker swarm- Switches of
docker container runcommand like -i (interactive), -t (pseud terminal), -d (detached), -p (publish port) etc supported here.
- Switches of
docker service ls: List services- –filter, –format and -q (quiet) switches which we saw above are supported with this command.
docker service ps: Lists tasks of services- –filter, –format and -q (quiet) switches which we saw above are supported with this command.
docker service logs: Display logs of service or tasksdocker service rm: Remove service- -f : Force remove
docker service update: Update service config- Most of the parameters defined in service create command can be updated here.
docker service rollback: Revert back changes done in service config.docker service scale: Scale one or more replicated services.- servicename=number format
docker service inspect: Detailed information about service.
